Released the latest Oracle 1Z0-1085-20 exam dumps! You can get 1Z0-1085-20 VCE dumps and 1Z0-1085-20 PDF dumps from Pass4itsure, (including the latest 1Z0-1085-20 exam questions), which will ensure that your 1Z0-1085-20 exam is 100% passed! Pass4itsure 1Z0-1085-20 dumps VCE and PDF — https://www.pass4itsure.com/1z0-1085-20.html Updated!
Oracle 1Z0-1085-20 Exam Dumps
[100% free] Oracle 1Z0-1085-20 pdf dumps https://drive.google.com/file/d/1fS2XqkGs2L0kKe-j7ILGFF65OCOLIv_8/view?usp=sharing
Oracle Cloud 1Z0-1085-20 Practice Test 1-13
QUESTION 1
Which service is the most effective for moving large amounts of data from your on-premises to Oracle Cloud
Infrastructure (OCI)?
A. Data Safe
B. Dynamic Routing Gateway
C. Data Transfer appliance
D. Internet Gateway
Correct Answer: C
APPLIANCE-BASED DATA TRANSFER You send your data as files on secure, high-capacity, Oracle-supplied storage
appliances to an Oracle transfer site. Operators at the Oracle transfer site upload the data into your designated Object
Storage bucket in your tenancy. This solution supports data transfer when you are migrating a large volume of data and
when using disks is not a practical alternative. You do not need to write any code or purchase any hardware. Oracle
supplies the transfer appliance and software required to manage the transfer. https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/enus/iaas/Content/DataTransfer/Concepts/overview.htm Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Data Transfer Appliance securely
moves terabytes or petabytes data between on-premise data centers and the cloud. The service reduces data migration
times from weeks or months to just hours and is available for data import to the cloud and data export from the cloud.
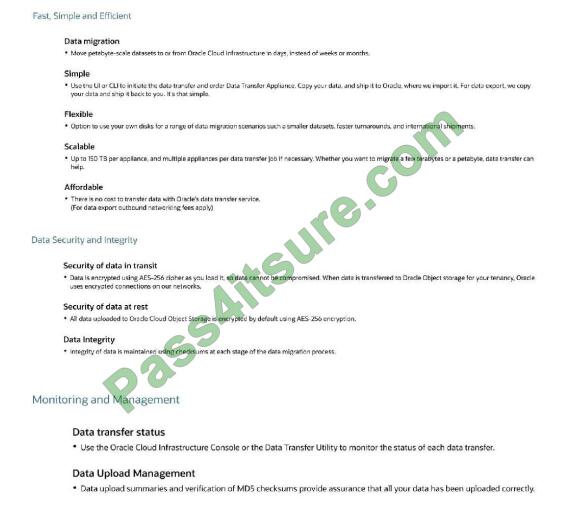
Reference: Click here
QUESTION 2
Which kind of scaling is supported by virtual machines in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute service?
A. Only scaling up or down
B. Only scaling out
C. Scaling up or down and scaling in or out
D. Only scaling in
Correct Answer: C
Horizontal scaling means that you scale by adding more machines into your pool of resources whereas Vertical scaling
means that you scale by adding more power (CPU, RAM) to an existing machine. An easy way to remember this is to
think of a machine on a server rack, we add more machines across the horizontal direction and add more resources to a
the machine in the vertical direction.
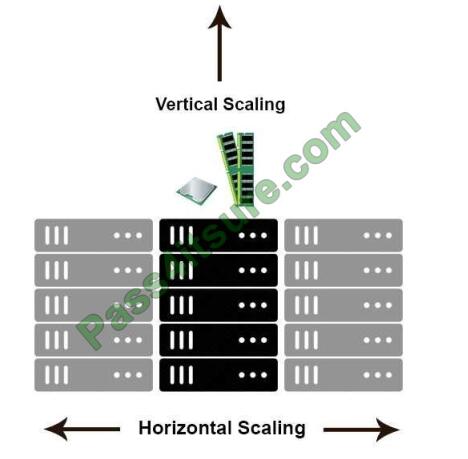
With horizontal-scaling it is often easier to scale dynamically by adding more machines into the existing pool — Verticalscaling is often limited to the capacity of a single machine, scaling beyond that capacity often involves downtime and
comes with an upper limit.
Reference: Click here
QUESTION 3
Which option provides the best performance for running OTLP workloads in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)?
A. OCI Autonomous Data Warehouse
B. OCI Virtual Machine Instance
C. OCI Dedicated Virtual Host
D. OCI Autonomous Transaction Processing
Correct Answer: D Click here
QUESTION 4
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure is compliant with which three industry standards?
A. SOC 1 Type 2 and SOC 2 Type 2 attestations
B. NERC Critical Infrastructure Protection Standards
C. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
D. ISO 27001:2013 certification
E. Health Care Compliance Association (HCCA)
Correct Answer: ACD
Here is the official list of all industry standards that OCI complies with click here
QUESTION 5
Which feature is not a component of Oracle cloud Infrastructure identity and Access management service?
A. federation
B. User Credential
C. Network Security Group
D. Policies
Correct Answer: C
Components of IAM RESOURCE The cloud objects that your company\\’s employees create and use when interacting
with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. For example: compute instances, block storage volumes, virtual cloud networks
(VCNs), subnets, route tables, etc. USER An individual employee or system that needs to manage or use your
company\\’s Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources. Users might need to launch instances, manage remote disks, work
with your virtual cloud network, etc. End-users of your application are not typically IAM users. Users have one or more
IAM credentials (see User Credentials). GROUP A collection of users who all need the same type of access to a
particular set of resources or compartments. DYNAMIC GROUP A special type of group that contains resources (such as
compute instances) that match rules that you define (thus the membership can change dynamically as matching
resources are created or deleted). These instances act as “principal” actors and can make API calls to services
according to policies that you write for the dynamic group. NETWORK SOURCE A group of IP addresses that are
allowed to access resources in your tenancy. The IP addresses can be public IP addresses or IP addresses from a VCN
within your tenancy. After you create the network source, you use policy to restrict access to only requests that originate
from the IPs in the network source. COMPARTMENT A collection of related resources. Compartments are a
fundamental component of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure for organizing and isolating your cloud resources. You use them
to clearly separate resources for the purposes of measuring usage and billing, access (through the use of policies), and
isolation (separating the resources for one project or business unit from another). A common approach is to create a
compartment for each major part of your organization. For more information, see Setting Up Your Tenancy. TENANCY
The root compartment that contains all of your organization\\’s Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources. Oracle
automatically creates your company\\’s tenancy for you. Directly within the tenancy are your IAM entities (users, groups,
compartments, and some policies; you can also put policies into compartments inside the tenancy). You place the other
types of cloud resources (e.g., instances, virtual networks, block storage volumes, etc.) inside the compartments that
you create. POLICY A document that specifies who can access which resources, and how. Access is granted at the
group and compartment level, which means you can write a policy that gives a group a specific type of access within a
specific compartment, or to the tenancy itself. If you give a group access to the tenancy, the group automatically gets
the same type of access to all the compartments inside the tenancy. For more information, see Example Scenario and
How Policies Work. The word “policy” is used by people in different ways: to mean an individual statement written in the
policy language; to mean a collection of statements in a single, named “policy” document (which has an Oracle Cloud ID
(OCID) assigned to it), and to mean the overall body of policies your organization uses to control access to resources.
HOME REGION The region where your IAM resources reside. All IAM resources are global and available across all
regions, but the master set of definitions reside in a single region, the home region. You must make changes to your
IAM resources in your home region. The changes will be automatically propagated to all regions. For more information,
see Managing Regions. FEDERATION A relationship that an administrator configures between an identity provider and
a service provider. When you federate Oracle Cloud Infrastructure with an identity provider, you manage users and
groups in the identity provider. You manage authorization in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure\\’s IAM service. Oracle Cloud
Infrastructure tenancies are federated with Oracle Identity Cloud Service by default. Reference: Click here
QUESTION 6
A customer is looking to migrate their old database backups from their on-premises data center to Oracle Cloud
Infrastructure (OCI). Which OCI service is the most cost-effective?
A. Block Volume
B. Archive Storage
C. File Storage
D. Object Storage (standard)
Correct Answer: B
Archive storage is the most cost-effective for archive data Reference:
https://www.oracle.com/cloud/storage/archive-storage.html Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offers two distinct storage class
tiers to address the need for both performant, frequently accessed “hot” storage, and less frequently accessed “cold”
storage. Storage tiers help you maximize performance where appropriate and minimize costs where possible.
1) Use Archive Storage for data to which you seldom or rarely access, but that must be retained and preserved for long
periods of time. The cost-efficiency of the Archive Storage offsets the long lead time required to access the data.
2) Use Object Storage for data to which you need fast, immediate, and frequent access. Data accessibility and
performance justify a higher price to store data in the Object Storage. For more information, see Overview of Object
Storage.

Reference: Click here
QUESTION 7
Which Oracle cloud infrastructure capability can be used to protect against power failures within an availability Domain?
A. Data Plane
B. Fault Domains
C. Services Cells
D. Top of Rack Switch
Correct Answer: B
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain
contains three fault domains. Fault domains provide anti-affinity: they let you distribute your instances so that the
instances are
not on the same physical hardware within a single availability domain. A hardware failure or Compute hardware
maintenance event that affects one fault domain does not affect instances in other fault domains. In addition, the
physical hardware in a fault domain has independent and redundant power supplies, which prevents a failure in the power supply
hardware within one fault domain from affecting other fault domains. To control the placement of your computes
instances, bare metal DB system instances, or virtual machine DB system instances, you can optionally specify the fault
domain for a new instance or instance pool at launch time. If you don\\’t specify the fault domain, the system selects
one
for you. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure makes a best-effort anti-affinity placement across different fault domains while
optimizing for available capacity in the availability domain. To change the fault domain for an instance, terminate it and
launch
a new instance in the preferred fault domain.
Use fault domains to do the following things:
Protect against unexpected hardware failures or power supply failures. Protect against planned outages because of
Computer hardware maintenance.
Reference: Click here
QUESTION 8
Which two security capabilities are offered by Oracle Cloud Infrastructure?
A. Always on data encryption for data-at-rest.
B. Certificate Management service
C. Captcha
D. Key Management service
E. Managed Active Directory service
Correct Answer: AD
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure\\’s security approach is based on seven core pillars. Each pillar has multiple solutions
designed to maximize the security and compliance of the platform and to help customers to improve their security
posture. High Availability: Offer fault-independent data centers that enable high-availability scale-out architectures and
are resilient against network attacks, ensuring constant uptime in the face of disaster and security attacks. Customer
Isolation: Allow customers to deploy their application and data assets in an environment that commits full isolation from
other tenants and Oracle\\’s staff. Data Encryption: Protect customer data-at-rest and in-transit in a way that allows
customers to meet their security and compliance requirements with respect to cryptographic algorithms and key
management. Security Controls: Offer customers effectively and easy-to-use application, platform, and network security
solutions that allow them to protect their workloads, have a secure application delivery using a global edge network,
constrain access to their services, and segregate operational responsibilities to reduce the risk associated with
malicious and accidental user actions. Visibility: Offer customers comprehensive log data and security analytics that
they can use to audit and monitor actions on their resources, allowing them to meet their audit requirements and reduce
security and operational risk. Secure Hybrid Cloud: Enable customers to use their existing security assets, such as user
accounts and policies, as well as third-party security solutions when accessing their cloud resources and securing their
data and application assets in the cloud. Verifiably Secure Infrastructure: Follow rigorous processes and use effective
security controls in all phases of cloud service development and operation. Demonstrate adherence to Oracle\\’s strict
security standards through third-party audits, certifications, and attestations. Help customers demonstrate compliance
readiness to internal security and compliance teams, their customers, auditors, and regulators. Reference: Click here
QUESTION 9
You are required to host several files in a location that can be publicly accessible from anywhere in the world. Which
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) service should you use?
A. OCI Object Storage
B. Oracle Functions
C. OCI Block Volume
D. OCI File Storage
E. OCI Storage Gateway
Correct Answer: A
QUESTION 10
Which is NOT required to register and log support requests in My Oracle Support (MOS)?
A. Your Customer Support Identifier (CSl)
B. Your account password
C. Your tenancy OCID (Oracle Cloud Identifier)
D. Your resource OCID (Oracle Cloud Identifier)
Correct Answer: D
You can open a support service request with Oracle Support To create a service request:
Go to My Oracle Support and sign in.
If you are not signed in to Oracle Cloud Support, click Switch to Cloud Support at the top of the page.
Click Create Service Request.
Select the following from the displayed menus:
Service Type: Select Oracle Cloud Infrastructure from the list. Service Name: Select the appropriate option for your
organization. Problem Type: Select your problem type from the list.
Enter your contact information.
Enter a Description, and then enter the required fields specific to your issue. For most Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
issues you need to include the OCID (Oracle Cloud Identifier) for each resource you need help with. See Locating
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure IDs for instructions on locating these.
Reference: Click here
QUESTION 11
Your company has deployed a business critical application in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. What should you do to ensure
that your application has the highest level of resilience and availability?
A. Deploy the application across multiple Availability Domains and Subnets
B. Deploy the application across multiple Virtual Cloud Networks
C. Deploy the application across multiple Regions and Availability Domains
D. Deploy the application across multiple Availability Domains and Fault Domains
Correct Answer: C
To design a high availability architecture, three key elements should be considered– redundancy, monitoring, and
failover: 1) Redundancy means that multiple components can perform the same task. The problem of a single point of
failure is eliminated because redundant components can take over a task performed by a component that has failed. 2)
Monitoring means checking whether or not a component is working properly. 3) Failover is the process by which a
secondary component becomes primary when the primary component fails. The best practices introduced here focus on
these three key elements. Although high availability can be achieved at many different levels, including the application
level and the cloud infrastructure level, here we will focus on the cloud infrastructure level. An Oracle Cloud
Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area composed of one or more availability domains, each composed of
three fault domains. High availability is ensured by a redundancy of fault domains within the availability domains. An
availability domain is one or more data centers located within a region. Availability domains are isolated from each
other, fault-tolerant, and unlikely to fail simultaneously. Because availability domains do not share physical
infrastructure, such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network, a failure that impacts one availability
domain is unlikely to impact the availability of others. A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within
an availability domain. Each availability domain contains three fault domains. Fault domains let you distribute your
instances so that they are not on the same physical hardware within a single availability domain. As a result, an
unexpected hardware failure or a Compute hardware maintenance that affects one fault domain does not affect
instances in other fault domains. You can optionally specify the fault domain for a new instance at launch time, or you
can let the system select one for you. All the available domains in a region are connected to each other by a low-latency, high bandwidth network. This predictable, encrypted interconnection between availability domains provides the
building blocks for both high availability and disaster recovery. Reference: Click here
QUESTION 12
What does compute instance vertical scaling mean?
A. Providing Fault tolerance
B. Adding additional compute instances
C. Enabling Disaster recovery
D. Changing to a large or smaller shape
Correct Answer: D
Changing the Shape of an Instance (Horizontal Scaling)
You can change the shape of a virtual machine (VM) instance without having to rebuild your instances or redeploy your
applications. This lets you scale up your Compute resources for increased performance, or scale down to reduce
cost.Autoscaling (vertical scaling)
Autoscaling lets you automatically adjust the number of Compute instances in an instance pool based on performance
metrics such as CPU utilization. This helps you provide consistent performance for your end-users during periods of
high
demand, and helps you reduce your costs during periods of low demand.
As load increases, instances are automatically provisioned: the instance pool scales out. As load decreases, instances
are automatically removed: the instance pool scales in.


QUESTION 13
Which three components are part of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) identity and access management service?
A. Regional Subnets
B. Policies
C. Users
D. Compute Instances
E. Dynamic Groups
F. Roles
G. Virtual Cloud Networks
Correct Answer: BCE
Components of IAM IAM uses the components described in this section. To better understand how the components fit
together, see Example Scenario. RESOURCE The cloud objects that your company\\’s employees create and use when
interacting with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. For example: compute instances, block storage volumes, virtual cloud
networks (VCNs), subnets, route tables, etc. USER An individual employee or system that needs to manage or use your
company\\’s Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources. Users might need to launch instances, manage remote disks, work
with your virtual cloud network, etc. End-users of your application are not typically IAM users. Users have one or more
IAM credentials (see User Credentials). GROUP A collection of users who all need the same type of access to a
particular set of resources or compartments. DYNAMIC GROUP A special type of group that contains resources (such as
compute instances) that match rules that you define (thus the membership can change dynamically as matching
resources are created or deleted). These instances act as “principal” actors and can make API calls to services
according to policies that you write for the dynamic group. NETWORK SOURCE A group of IP addresses that are
allowed to access resources in your tenancy. The IP addresses can be public IP addresses or IP addresses from a VCN
within your tenancy. After you create the network source, you use policy to restrict access to only requests that originate
from the IPs in the network source. COMPARTMENT A collection of related resources. Compartments are a
fundamental component of Oracle Cloud Infrastructure for organizing and isolating your cloud resources. You use them
to clearly separate resources for the purposes of measuring usage and billing, access (through the use of policies), and
isolation (separating the resources for one project or business unit from another). A common approach is to create a
compartment for each major part of your organization. For more information, see Setting Up Your Tenancy. TENANCY
The root compartment that contains all of your organization\\’s Oracle Cloud Infrastructure resources. Oracle
automatically creates your company\\’s tenancy for you. Directly within the tenancy are your IAM entities (users, groups,
compartments, and some policies; you can also put policies into compartments inside the tenancy). You place the other
types of cloud resources (e.g., instances, virtual networks, block storage volumes, etc.) inside the compartments that
you create. POLICY A document that specifies who can access which resources, and how. Access is granted at the
group and compartment level, which means you can write a policy that gives a group a specific type of access within a
specific compartment, or to the tenancy itself. If you give a group access to the tenancy, the group automatically gets
the same type of access to all the compartments inside the tenancy. For more information, see Example Scenario and
How Policies Work. The word “policy” is used by people in different ways: to mean an individual statement written in the
policy language; to mean a collection of statements in a single, named “policy” document (which has an Oracle Cloud ID
(OCID) assigned to it), and to mean the overall body of policies your organization uses to control access to resources.
HOME REGION The region where your IAM resources reside. All IAM resources are global and available across all
regions, but the master set of definitions reside in a single region, the home region. You must make changes to your
IAM resources in your home region. The changes will be automatically propagated to all regions. For more information,
see Managing Regions. FEDERATION A relationship that an administrator configures between an identity provider and a service provider. When you federate Oracle Cloud Infrastructure with an identity provider, you manage users and
groups in the identity provider. You manage authorization in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure\\’s IAM service. Oracle Cloud
Infrastructure tenancies are federated with Oracle Identity Cloud Service by default.
Click here
Click here to view other exam dumps questions.
Pass4itsure Discount Code 2020
Please read the picture carefully to get 12% off!

P.S.
Passing the Oracle 1Z0-1085-20 exam is no more dream. Free share all the resources: Latest 1Z0-1085-20 practice questions, latest 1Z0-1085-20 pdf dumps, 1Z0-1085-20 exam video learning. Visit https://www.pass4itsure.com/1z0-1085-20.html exam dumps with the latest questions.
